If you want to install the device on a Settopbox please follow this link:
http://support.sundtek.com/index.php/topic,348.0.htmlNow back to the installation on a regular Linux based system:
Sundtek MediaTV Pro/Gold are the world's first USB DVB-C, DVB-T, AnalogTV, Composite, S-Video, FM-Radio devices which are fully supported with Linux, our technology provides support for the entire 2.6.x Linux Kernel Series, unpatched Kernels are supported from 2.6.15 on. An installation usually takes a few seconds only.
http://www.sundtek.com/docs/sundtek_smart_facts.pdfhttp://www.sundtek.com/docs/sundtek-architecture.pdfThe driver installation is currently mainly done on the console, we are working on providing a graphical installer lateron. The driver is developed by Sundtek Ltd. and runs as normal application (in userspace), if unexpected problems occur the system will not be affected by it, aside of that it has the advantage that it is not bound to any particular kernel version which makes difficult compiling unnecessary.
Minimum System requirements Linux 2.6.15/libc2.4+ 32 or 64 bit (which is basically supported by all distributions which have been available for the last 4 years/since 2006), 1.5 Ghz
Supported Architectures:






* Intel/AMD x86 (32/64 bit)
* ARM (eg. Sheevaplug)
* IBM PowerPC (eg. Sony Playstation 3 - first revision)
* MIPS
* MIPSel (eg. Dreambox)
* further builds are available uppon request
This installer supports following operating systems:



* Linux (Ubuntu, Redhat, Suse, Fedora, Mandriva, Gentoo, Mint, etc. die Software funktioniert uebergreifend und ist an keine spezielle Version gebunden).
* FreeBSD 8.0 (will be released soon)
* Apple (Sundtek MediaTV Gold/will be released soon, mediaclient commands will work, although the Apple support comes with an extra Mac based installer and extra TV application)
Please note that the linux 2.6.27 and 2.6.28 series have a bug in the USB System wich makes the memory usage of the Linux system grow, this causes the system to run out of memory after some time. You can read more about this issue and how to fix it on the
Linux USB Mailinglist, it is probably easier to use Linux 2.6.15 - 2.6.26 or 2.6.29+.
The latest driver version can be downloaded from the
Driver BoardIn case you do not have a device but already want to play around with it, you can try to use our virtual demo driver which supports emulating video devices. After the installation just run "/opt/bin/mediaclient --tvdummy" for creating a virtual driver instance.
Screenshotopen a console and run following line as root
$ wget http://www.sundtek.de/media/sundtek_netinst.sh
$ chmod 777 sundtek_netinst.sh
$ sudo ./sundtek_netinst.sh
Welcome to the Sundtek linux driver setup
Legal notice:
This software comes without any warranty, use it at your own risk
Nutzungsbedingungen:
Sundtek übernimmt keinerlei Haftung für Schäden welche eventuell durch
das System oder die angebotenen Dateien entstehen können.
Do you want to continue [Y/N]:
Wollen Sie fortfahren [J/N]:
y
stopping old driver instance...
installing em28xx driver to /opt
unpacking...
checking system... 64Bit System detected
installing...
finalizing configuration... (can take a few seconds)
installing libmediaclient interception library
Starting driver...
done.
If you just want to use the device quickly you can install our streaming server by running:
/opt/bin/mediaclient --installstreamer
Afterwards open your webbrowser and go to
http://localhost:22000The menu will guide you through the setup, and you'll be able to watch TV using VLC within a few minutes.
Available playlists after scanning:
http://localhost:22000/freesdtv.m3uhttp://localhost:22000/freehdtv.m3uhttp://localhost:22000/radio.m3ufor identifying the device in the system you can run following command:
$ /opt/bin/mediaclient -e
**** List of Media Hardware Devices ****
device 0: [ Sundtek MediaTV Pro] DVB-C, DVB-T, ANALOG-TV, FM-RADIO, REMOTE-CONTROL, OSS-AUDIO, RDS
[DVB-C]:
FRONTEND: /dev/dvb/adapter0/frontend0
DVR: /dev/dvb/adapter0/dvr0
DMX: /dev/dvb/adapter0/demux0
[DVB-T]:
FRONTEND: /dev/dvb/adapter0/frontend0
DVR: /dev/dvb/adapter0/dvr0
DMX: /dev/dvb/adapter0/demux0
[ANALOG-TV]:
VIDEO0: /dev/video1
VBI0: /dev/vbi0
[FM-RADIO]:
RADIO0: /dev/radio0
RDS: /dev/rds0
[REMOTECONTROL]:
INPUT0: /dev/mediainput0
[OSS]:
OSS0: /dev/dsp0
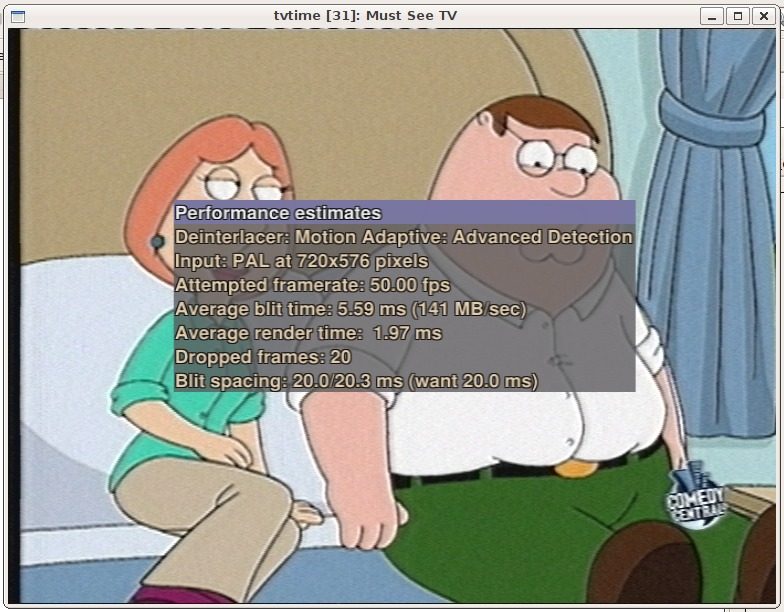
DeinterlacingDeinterlacing is also supported:
Original (scrolling text):

Sundtek Enhanced Quality:

Activate deinterlacer:
$ /opt/bin/mediaclient -d /dev/video1 --vfilter=on
Deinterlacer deaktivieren:
$ /opt/bin/mediaclient -d /dev/video1 --vfilter=off
Analogue TV/Composite/S-Videofor starting analogTV with tvtime:
tvtime -d /dev/video1
by default most linux tv players do not support digital audio properly, in order to fix that problem our driver supports internal audio processing, which means that the driver automatically tries to play the available data to the default soundcard, while the TV application is just in charge of displaying the video.
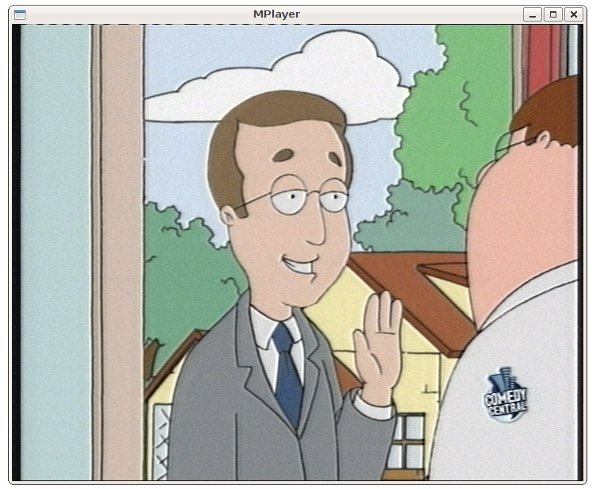
For using the device with mplayer:
$ mplayer tv:// -tv driver=v4l2:device=/dev/video1
MPlayer SVN-r29305-4.3.2 (C) 2000-2009 MPlayer Team
Playing tv://.
TV file format detected.
Selected driver: v4l2
name: Video 4 Linux 2 input
author: Martin Olschewski <olschewski@zpr.uni-koeln.de>
comment: first try, more to come ;-)
Selected device: Sundtek MediaTV
Tuner cap: STEREO
Tuner rxs:
Capabilites: video capture VBI capture device tuner audio read/write streaming
supported norms: 0 = PAL-BG; 1 = PAL-DK; 2 = PAL-I; 3 = PAL-M; 4 = NTSC-M;
inputs: 0 = Television; 1 = Composite; 2 = S-Video;
Current input: 0
Current format: YUYV
The driver automatically tries to figure out the correct audio playback.

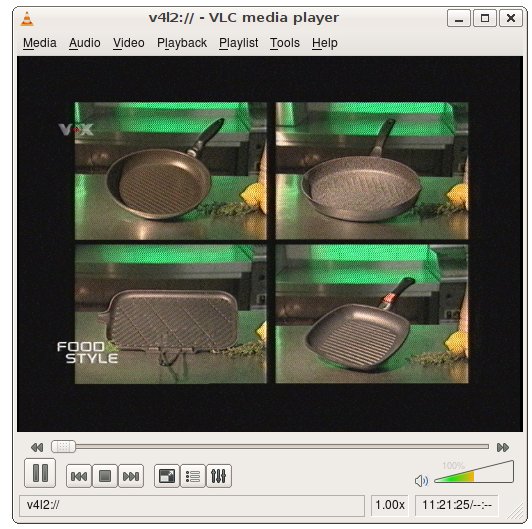
For using analogue TV with vlc, just start up VLC and select the corresponding capturedevice eg. /dev/video1 in our case
 FM Radio
FM Radioon the terminal using mediaclient:
/opt/bin/mediaclient -f 90100000 -m RADIO -d /dev/radio0 -t 0
/opt/bin/mediaclient -m RADIO -d /dev/radio0 -c internal
/opt/bin/mediaclient -m RADIO -d /dev/radio0 --mute off
for disabling audio in the background:
/opt/bin/mediaclient -m RADIO -d /dev/radio0 --mute on
Console Application:
$ radio -c /dev/radio0
GUI Application (gnomeradio):
 DVB-TKaffeine
DVB-TKaffeinethe device has to be switched to DVB-T, this only has to be done once for using DVB-T:
$ /opt/bin/mediaclient --setdtvmode=DVBT
$ kaffeine
 VDR
VDR(VDR also works with DVB-C)
$ /opt/bin/mediaclient --setdtvmode=DVBT
$ vdr -P "xineliboutput --local=sxfe --video=xshm --local=none --primary --remote=127.0.0.1:37890" -v /var/lib/video.00/ -l 3
 mplayer
mplayerto switch the device to dvb-t mode
$ /opt/bin/mediaclient -D DVBT
$ scan dvb-apps/util/scan/dvb-t/de-Berlin
scanning dvb-apps/util/scan/dvb-t/de-Berlin
using '/dev/dvb/adapter0/frontend0' and '/dev/dvb/adapter0/demux0'
Frontend can not do INVERSION_AUTO, trying INVERSION_OFF instead
initial transponder 506000000 0 2 9 1 1 2 0
initial transponder 522000000 0 2 9 1 1 2 0
initial transponder 570000000 0 2 9 1 1 3 0
initial transponder 658000000 0 2 9 1 1 2 0
initial transponder 754000000 0 2 9 1 1 2 0
initial transponder 778000000 0 2 9 1 1 2 0
>>> tune to: 506000000:INVERSION_OFF:BANDWIDTH_8_MHZ:FEC_2_3:FEC_AUTO:QAM_16:TRANSMISSION_MODE_8K:GUARD_INTERVAL_1_8:HIERARCHY_NONE
0x0000 0x4015: pmt_pid 0x0150 RTL World -- RTL Television (running)
0x0000 0x4016: pmt_pid 0x0160 RTL World -- RTL2 (running)
0x0000 0x401b: pmt_pid 0x01b0 RTL World -- Super RTL (running)
0x0000 0x4022: pmt_pid 0x0220 RTL World -- VOX (running)
Network Name 'MEDIA BROADCAST'
etc.
$ /opt/bin/mediaclient -m DVBT -f 506000000 -b 8
Using device: /dev/dvb/adapter0/frontend0
Checking for lock:
. [LOCKED]
$ mplayer /dev/dvb/adapter0/dvr0
oder
$ cat /dev/dvb/adapter0/dvr0 | mplayer -cache 10240 -
 DVB-Ckaffeine
DVB-Ckaffeinefor DVB-C the device has to be switched to DVB-C first by using the mediaclient command:
$ /opt/bin/mediaclient --setdtvmode=DVBC
$ kaffeine
 mplayer
mplayerTo switch the device to dvb-c mode:
$ /opt/bin/mediaclient -D DVBC
$ scan dvb-apps/util/scan/dvb-c/de-Berlin
scanning dvb-apps/util/scan/dvb-c/de-Berlin
using '/dev/dvb/adapter0/frontend0' and '/dev/dvb/adapter0/demux0'
initial transponder 113000000 6900000 0 3
initial transponder 346000000 6900000 0 5
initial transponder 522000000 6900000 0 5
initial transponder 402000000 6900000 0 5
initial transponder 378000000 6900000 0 3
initial transponder 378000000 6900000 0 3
initial transponder 394000000 6900000 0 3
initial transponder 466000000 6900000 0 3
>>> tune to: 113000000:INVERSION_AUTO:6900000:FEC_NONE:QAM_64
0x0000 0x6dca: pmt_pid 0x0064 ARD -- Das Erste (running)
0x0000 0x6dcb: pmt_pid 0x00c8 ARD -- Bayerisches FS Süd (running)
0x0000 0x6dcc: pmt_pid 0x012c ARD -- hr-fernsehen (running)
0x0000 0x6dce: pmt_pid 0x01f4 ARD -- Bayerisches FS Nord (running)
0x0000 0x6dcf: pmt_pid 0x0258 ARD -- WDR Köln (running)
0x0000 0x6dd0: pmt_pid 0x02bc ARD -- BR-alpha* (running)
0x0000 0x6dd1: pmt_pid 0x0320 ARD -- SWR Fernsehen BW (running)
$ /opt/bin/mediaclient -m DVBC -f 113000000 -S 6900000 -M Q64
Using device: /dev/dvb/adapter0/frontend0
Checking for lock:
. [LOCKED]
$ mplayer /dev/dvb/adapter0/dvr0
oder
$ cat /dev/dvb/adapter0/dvr0 | mplayer -cache 10240 -

high resolution screenshot:
http://sundtek.com/images/dvbc-full.jpgto remove the driver from the system:
./sundtek_installer.sh -u
Sundtek em28xx linux driver setup
stopping em28xx driver...
removing driver
.......
driver successfully removed from system
PowersavingThe powersaving will be activated after 15 seconds of inactivity, after this time the device will start to cool down. Powersaving also increases the lifetime of the USB TV device.
Troubleshootingit's possible that some applications already access the device driver during the bootup. This will cause the device to be set to the corresponding device mode.
To check which applications are accessing the driver you can run following command:
$ /opt/bin/mediaclient --lc
**** List of Media Clients ****
/dev/dvb/adapter0/frontend0:
No client connected
/dev/dvb/adapter0/dvr0:
No client connected
/dev/dvb/adapter0/demux0:
No client connected
/dev/video1:
329 ... tvtime
/dev/vbi0:
No client connected
/dev/radio0:
No client connected
/dev/mediainput0:
No client connected
/dev/dsp0:
28289 ... mediasrv
please note tvtime does not support audio playback by itself, the multimedia framework itself is taking care about it, this also shows up the audio process being connected to the driver.
In order to disconnect (not to kill) tvtime from the driver following command can be used:
$ /opt/bin/mediaclient --dc 329
PulseaudioThere are some useful pulseaudio tools available (for example pavucontrol). Pavucontrol allows to individually configure the audio volume. Since pulseaudio is not stable yet it might happen that the driver switches back to Alsa during the runtime.
pavucontrol:
pavumeter:
NVidia graphicdrivers:
http://www.nvidia.de/Download/index.aspx?lang=deATI graphicdrivers:
http://support.amd.com/de/gpudownload/Pages/index.aspxRestricted Formats/Codecs Suse:
http://opensuse-community.org/Restricted_Formats/11.0http://opensuse-community.org/Restricted_Formats/11.1----
Signalstrength:By default the signalreporting returns 0% or 100%, this can be changed to a more accurate signalreporting by using following command:
/opt/bin/mediaclient --signalreporting=1
(inaccurate reporting does not take such a long time to read the information from the device, with more accurate signalreporting mplayer won't run smoothly)
Syntax:
/opt/bin/mediaclient -d /dev/video[n] --readsignal=[i]
whereas n is the videodevice (accordingly to /opt/bin/mediaclient -e) and i how often the signal should be read. If i is smaller or equal 0 the signalstatistics will only stop when the user interrupts the application.
Sample output:
SIGNAL: [.............................................................................................. ] 62225 (94%)
SIGNAL: [......................................................................................... ] 58950 (89%)
SIGNAL: [.............................................................................................. ] 62225 (94%)
SIGNAL: [.............................................................................................. ] 62225 (94%)
SIGNAL: [.............................................................................................. ] 62225 (94%)
SIGNAL: [............................................................................................ ] 60915 (92%)
----
In order to decompress the drivers (eg. for a manual installation):
$ ./sundtek_installer.sh -e
----
By default NULL packets (0x1fff) are filtered, in order to disable filtering following command can be used:
$ /opt/bin/mediaclient -d /dev/dvb/adapter0/frontend0 --nullpackets=on
----
In order to automatically start an application when the device gets plugged in or removed:
The configurationfile /etc/sundtek.conf can contain 2 parameters, device_attach and device_detach.
Those parameters can be used to start or reinitialize applications after the driver initialized a device.
Example:
/etc/sundtek.conf
device_attach=/usr/bin/usb_deviceattach.sh DEVID
device_detach=/usr/bin/usb_devicedetach.sh DEVID
DEVID will automatically be replaced with the device ID which is also returned by /opt/bin/mediaclient -e
----
Changing the transfermode for DVB-T/C from Isochronous to Bulk (some embedded PCs do not support Isochronous transfer with linux), this option can also work around some possible kernel isochronous bugs which are in 2.6.26-2.6.29 and 2.6.32.9 - 2.6.33.1.
By default when the devices are shipped, the device will be in Isochronous mode
In order to change the device to isochronous mode:
$ /opt/bin/mediaclient --dtvtransfermode=iso -d /dev/dvb/adapter0/frontend0
Setting transfermode to Isochronous
Please reconnect your device in order to activate the transfer mode change
To change it to Bulk:
$ /opt/bin/mediaclient --dtvtransfermode=bulk -d /dev/dvb/adapter0/frontend0
Setting transfermode to Bulk
Please reconnect your device in order to activate the transfer mode change
After switching the mode the device needs to be replugged
----
Hardware PID FilterIn order to use the hardware PID filter it needs to be enabled. The USB TV tuner supports up to 15 PID filters. The PID Filters can lower the required USB 2.0 bandwidth significantly - this is recommended for embedded PCs.
Enable Hardware PID filter:
/opt/bin/mediaclient -P on
Disable Hardware PID filter:
/opt/bin/mediaclient -P off
Show up the registered PID table:
$ /opt/bin/mediaclient -w
Using device: /dev/dvb/adapter0/frontend0
ID | PID
----------
0000 | 0x0001 - 1
0001 | 0x175c - 5980
0002 | 0x0899 - 2201
0003 | 0x089a - 2202
0004 | 0x089b - 2203
0005 | 0x0012 - 18
0006 | 0x1500 - 5376
0007 | 0x1501 - 5377
0008 | 0x1505 - 5381
The command which shows up which clients are connected now also shows up which PIDs are filtered:
$ /opt/bin/mediaclient --lc
**** List of Media Clients ****
/dev/dvb/adapter0/frontend0:
897 ... mediasrv
/dev/dvb/adapter0/dvr0:
897 ... mediasrv
/dev/dvb/adapter0/demux0:
897 ... mediasrv (0899)
897 ... mediasrv (089a)
897 ... mediasrv (089b)
897 ... mediasrv (0012)
897 ... mediasrv (1500)
897 ... mediasrv (1501)
897 ... mediasrv (1505)
897 ... mediasrv (0001)
897 ... mediasrv (175c)
/dev/video0:
No client connected
/dev/vbi0:
No client connected
/dev/radio0:
No client connected
/dev/rds0:
No client connected
/dev/mediainput0:
No client connected
/dev/dsp0:
No client connected